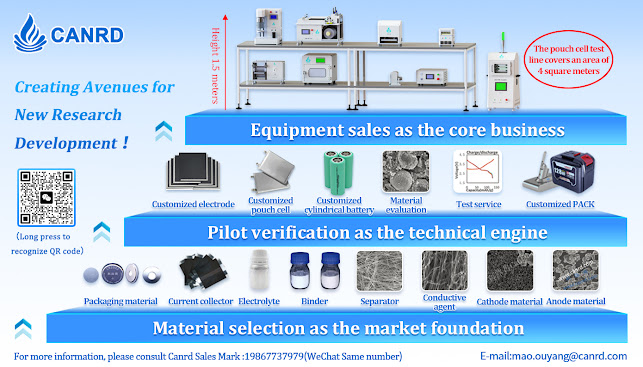
Lithium-ion batteries are mainly composed of five parts: positive electrode material, negative electrode material, diaphragm, electrolyte and packaging material. The lithium-ion battery diaphragm is a porous film with uniformly distributed micropores. It is located between the positive electrode material and the negative electrode material of lithium battery. It plays a role in preventing direct contact between positive and negative electrodes, preventing battery short circuit and transmitting ions. It is a key material to ensure battery safety and affect battery performance. Although the diaphragm does not directly participate in the electrochemical reaction of the battery, its performance affects the interface structure, internal resistance and other properties of the battery, and thus affects the battery's energy density, cycle life and rate performance; the thermal stability of the diaphragm also determines the battery's operating temperature tolerance range and battery safety. An ideal battery diaphragm should have good insulation, mechanical strength, electrochemical stability and thermal stability, as well as high porosity and appropriate pore size, and good wettability and adsorption properties for the electrolyte.
▲Lithium-ion battery (cylindrical) structure and lithium battery diaphragm