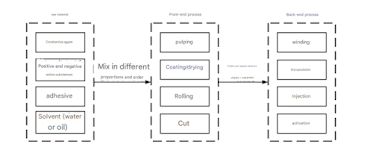
1. Lithium battery pole piece production process
The general process of lithium-ion battery pole piece manufacturing is : pulping, coating, drying, rolling, cutting, etc. The specific process flow is shown in the figure below.
2. Pulping
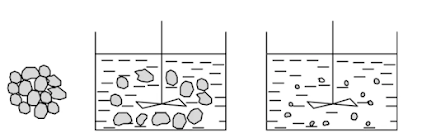
Pulping is the first process in the production of lithium-ion batteries. It is the process of uniformly dispersing the positive and negative active material powders, conductive agent powders, polymer binders and auxiliary agents in a solvent to form a stable slurry. Pulping has a great influence on the quality of and the electrochemical performance of lithium-ion batteries (greater than 30% ) . After the active material particle aggregates are broken up , they are dispersed in the solvent. The uniform and stable dispersion of active material particles in the slurry is the basic requirement for lithium-ion battery slurry. Whether the prepared slurry can be stably dispersed mainly depends on the force between the slurry particles. When the force between the particles is repulsive, spontaneous agglomeration basically does not occur, which helps the particles to be stably and evenly dispersed in the solvent; when the force between the particles is attractive, the active particles will spontaneously agglomerate, which is not conducive to stable and uniform dispersion.
When making slurry, the force on the particles needs to be controlled so that the particles can be stably and evenly dispersed. Common dispersion systems include oily systems and water-based systems. Both positive and negative electrode slurries can be prepared , while water-based systems are mainly used to prepare negative electrode slurries.
( 1 ) Shear coating. The current collector is located between the scraper and the roller surface, and the slurry is located on one side of the scraper. The current collector generates a shear force to coat the slurry on the surface of the current collector.
( 2 ) Wetting and leveling. Wetting is the process of the slurry spreading and adhering to the surface of the current collector. The slurry film on the surface has longitudinal stripes of uneven thickness. These stripes flow under the action of surface tension to make the slurry film flat. This is the leveling process.
( 3 ) Drying. The solvent of the slurry coated on the current collector evaporates by heating and is carried away by the air. As the solvent evaporates, the solid particles in the slurry approach each other to form a porous structure. The drying process is determined by many factors such as the solvent evaporation dynamics and the slurry flow characteristics, and has a great influence on the microstructure of the coating.
4. Roller pressing
Pole sheet rolling refers to the process in which the pole sheet, after coating and drying, passes through a roller press and is thinned under the action of rolling pressure. The pole sheet is pulled into the gap between the rollers by the friction between the rollers and the pole sheet. During rolling, the pole sheet's reduction rate will not be completely converted into the pole sheet's elongation rate. This is due to the porous nature of the pole sheet coating material. As the rolling process proceeds, the pole sheet coating particles will be rearranged and deformed to a certain extent. At this time, the coating density will increase, and the pole sheet elongation rate is much smaller than the elongation rate of dense metal.
The influence of electrode quality on battery performance during the preparation of lithium batteries
1.The impact of electrode production on battery performance
In the preparation process of lithium batteries, pole piece production is one of the links that has the greatest impact on battery performance. As the core component of lithium batteries, the quality of pole pieces directly affects the battery's capacity, internal resistance, cycle life and safety. The following are several key factors in the pole piece production process that have a significant impact on battery performance:
Coating process
Coating uniformity: Pole coating is the process of coating the slurry after the active material, conductive agent and binder are evenly mixed on the current collector (such as copper foil or aluminum foil). The uniformity of coating directly affects the battery capacity and the stability of battery performance. If the coating is uneven, the active material will be unevenly distributed, thus affecting the transmission efficiency of lithium ions and the battery capacity.
Coating parameter control: The control of temperature, speed, pressure and other parameters during the coating process is also crucial. For example, if the coating drying temperature is too low, the pole piece will not be completely dried, while if the temperature is too high, the coating on the pole piece surface may crack or fall off. Parameters such as coating surface density, size and thickness also need to be precisely controlled to avoid problems such as insufficient capacity, short circuit or increased internal resistance.
Pole design
Active material distribution: The active material must be evenly distributed on the electrode to ensure smooth lithium ion transmission inside the battery. Uneven distribution will lead to increased internal resistance, capacity loss and reduced charge and discharge efficiency.
Binder dosage: The amount of binder added needs to be moderate. Too much binder will block the gaps between active materials and hinder the transmission of lithium ions; too little binder may cause the active materials to fall off and affect battery performance.
Pole structure: The structural design of the pole piece needs to be reasonable, including the thickness and porosity of the pole piece, in order to optimize the transmission path and storage efficiency of lithium ions.
Drying and compaction
Drying process: The coated electrode needs to be dried to remove organic solvents and moisture. The temperature and time of the drying process must be strictly controlled to avoid deformation or cracking of the electrode.
Compacting process: The dried electrode needs to be compacted to improve its density and conductivity. The compacting process needs to be precisely controlled according to the electrode material and design requirements to avoid excessive compaction leading to electrode rupture or insufficient compaction leading to increased internal resistance.
Defect Control
Pole breakage: Pole breakage must be avoided during the manufacturing process to prevent the active material from falling off and the battery capacity from decreasing.
Impurity control: During the electrode production process, the environmental cleanliness must be strictly controlled to prevent dust, impurities, etc. from mixing into the electrode, so as not to affect battery performance and safety.
2.How much impact does the improvement of pole piece quality have on the performance of lithium batteries
Energy density and capacity
High-quality pole piece materials can significantly improve the energy density and capacity of lithium batteries. Energy density refers to the energy that can be stored in a battery per unit mass or unit volume, while capacity refers to the amount of charge that a battery can store and release. By optimizing the selection, ratio and structural design of pole piece materials, more active substances can be effectively utilized, thereby improving the energy density and capacity of the battery and extending the battery life.
Cycle life
Improving the quality of pole pieces also has an important impact on the cycle life of lithium batteries. Cycle life refers to the number of times a battery undergoes charge and discharge cycles under specific conditions until its capacity drops to a certain threshold. High-quality pole piece materials can maintain stable electrochemical properties, reduce losses and attenuation during the charge and discharge process, and thus extend the cycle life of the battery. This is especially important for application scenarios that require long-term use or frequent charge and discharge.
Security
The quality of the pole piece is also directly related to the safety of lithium batteries. Some inferior pole piece materials may cause the chemical reaction inside the battery to be too intense, generate too much heat, and even cause safety accidents such as battery overheating, fire or explosion. High-quality pole piece materials can reduce these risks and improve the safety performance of the battery. For example, by optimizing the coating material and structural design of the pole piece, the risk of thermal runaway during the charging and discharging process of the battery can be reduced, and the thermal stability and safety of the battery can be improved.
Charge and discharge performance
Improving the quality of the pole piece can also improve the charging and discharging performance of lithium batteries. The charging and discharging performance refers to the efficiency, stability and speed of the battery during the charging and discharging process. High-quality pole piece materials can reduce the internal resistance of the battery and improve the transmission efficiency of ions, making the battery more stable, fast and efficient during the charging and discharging process. This is of great significance for application scenarios that require fast charging or high power output.
3.Canrd Brief Introduce
Canrd use high battery R&D technology(core members are from CATL) and strong Chinese supply chain to help many foreign companies with fast R&D. We provide lab materials, electrodes, custom dry cells, material evaluation, perfomance and test, coin/pouch/cylindrical cell equipment line, and other R&D services.
Email: contact@canrd.com Phone/Wechat/WhatsApp: +86 19867737979
Canrd Official Web Canrd Company Vedio Canrd Company profile
Website : www.canrud.com














No comments:
Post a Comment