There are some theoretical introductions in this lecture, and not all of them have been experimented, so if there is anything wrong, please criticize and correct it.
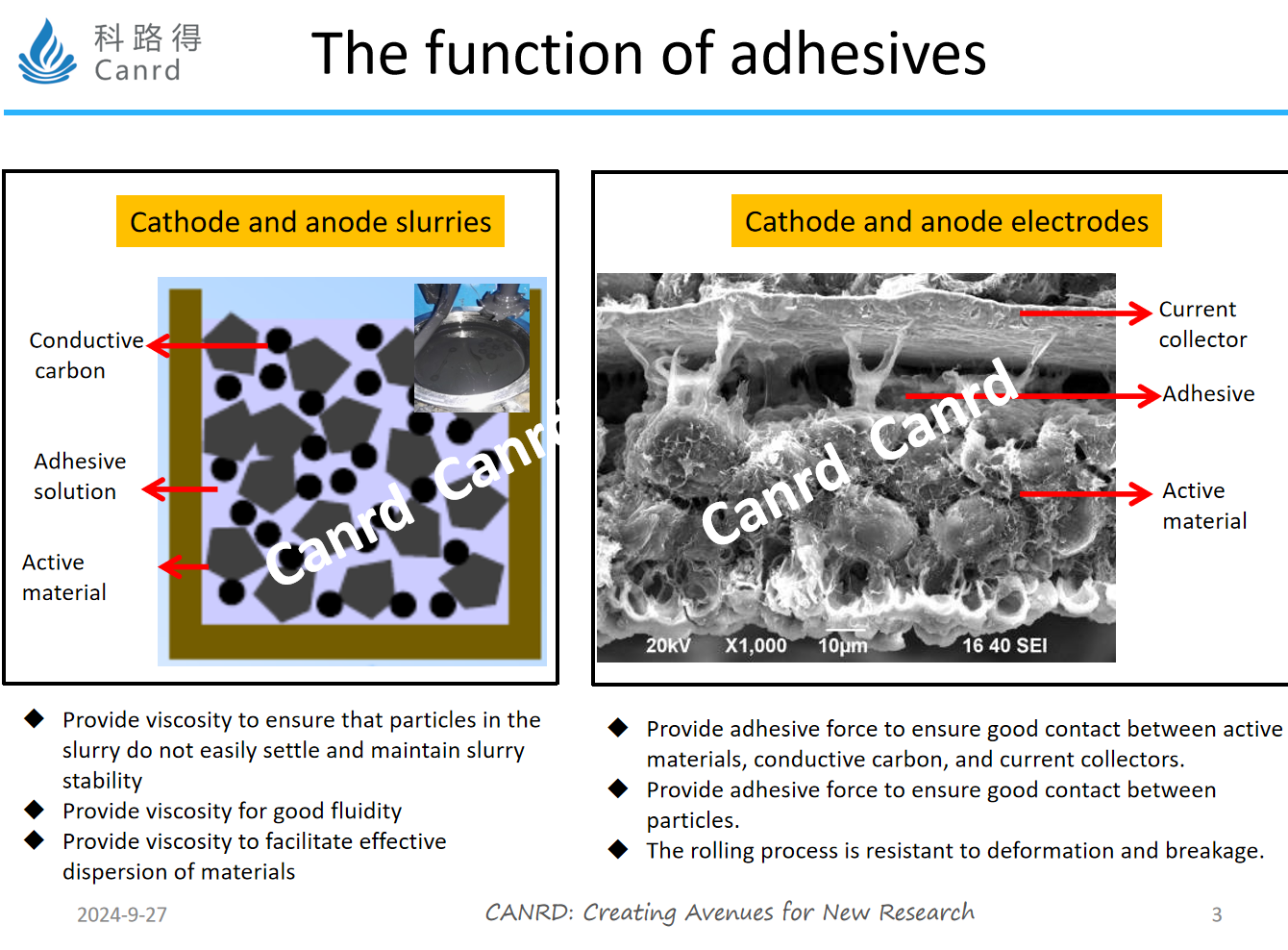
First, let's review the role of adhesives in the last lesson. In our practical application, it is mainly in the slurry and electrode - in the slurry, it is necessary to obtain a uniformly dispersed, well-flowed and stable slurry by binder; Good electronic contact between particles and between particles and current collectors should be ensured in the electrode.

There are many types of adhesives, which are divided into common and new adhesives, which vary according to different application fields and uses. As mentioned before, there are many types of adhesives, and each adhesive has different manufacturers and different models.
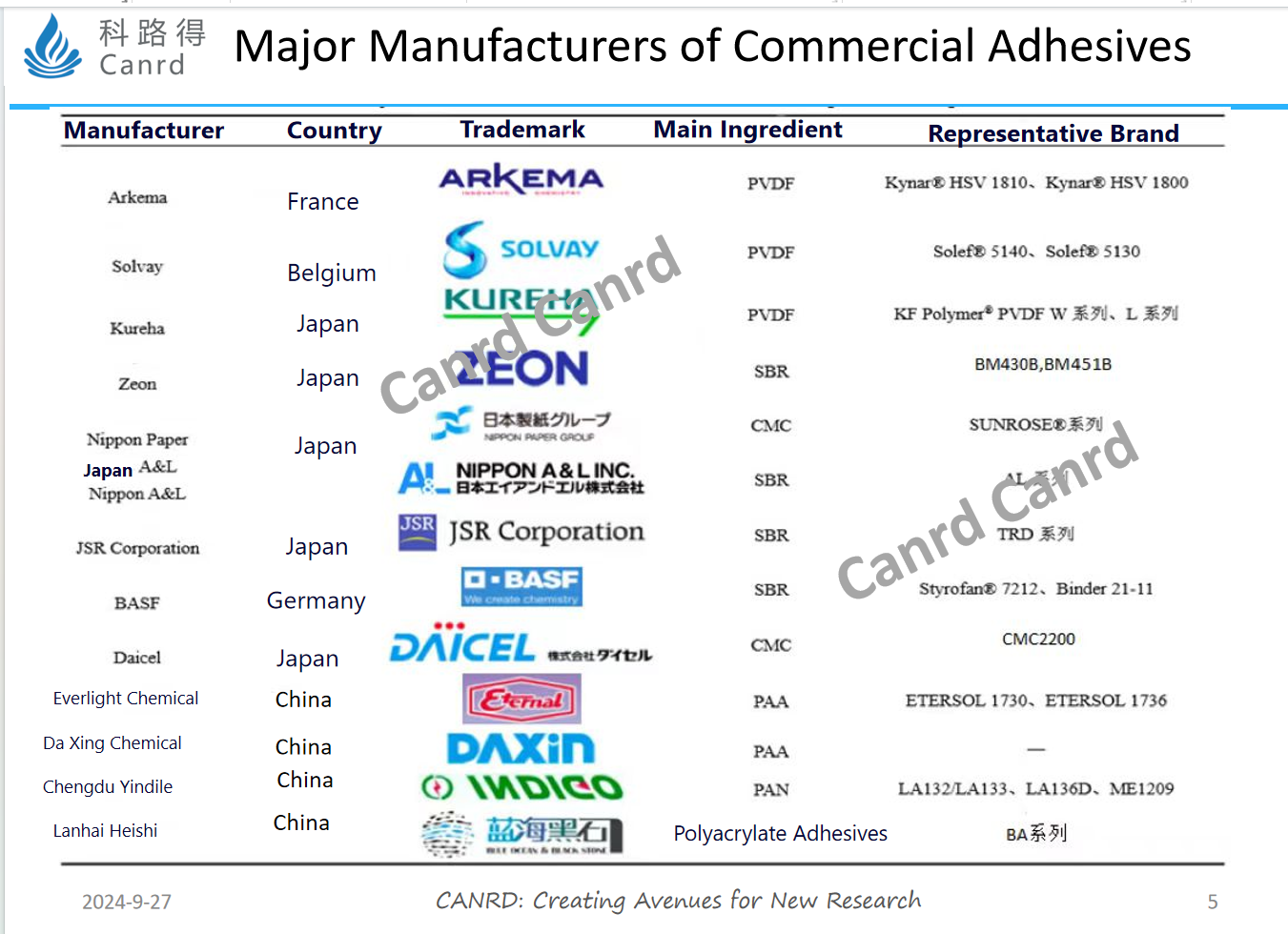
In this figure, there are many commercial adhesives such as PVDF, CMC, SBR, etc., each with different representative products.
With such a wide variety of adhesives, how do we choose the right one?
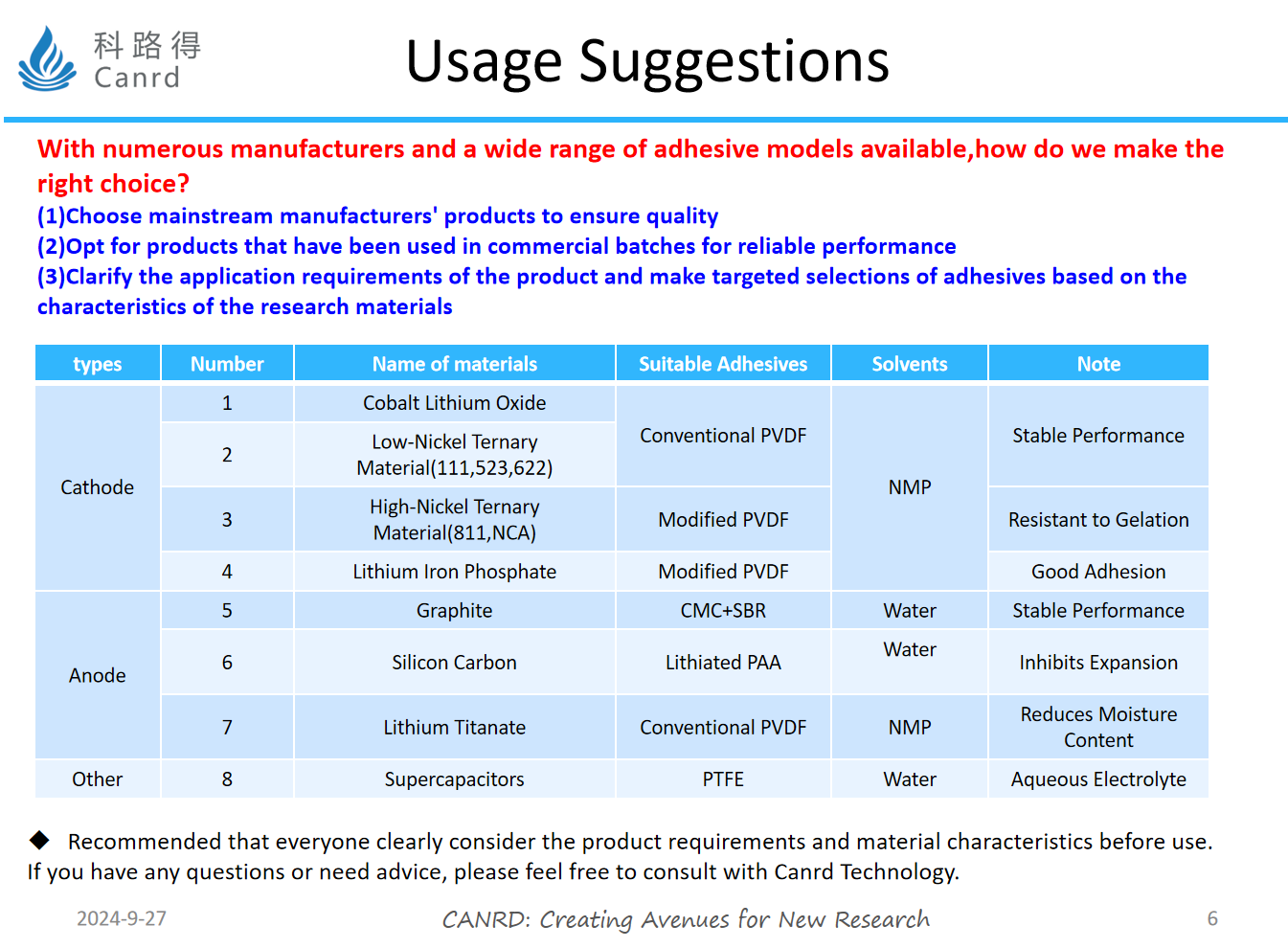
Here we give some suggestions. If you are not doing adhesive research, you should mainly find mainstream manufacturers, whose adhesives have quality assurance, and have been applied in large quantities with high reliability. For teachers who have special product needs or develop new materials, they need to make targeted choices according to specific requirements.
The following table lists the types of adhesives commonly used for different materials and solvents.
For some researchers who are engaged in battery product development, for example, to develop fast-charging batteries, then you need adhesives with good ionic conductivity; For the development of products with high energy density, it is necessary to respond to adhesives with large molecular weight, strong adhesion, and low dosage. Depending on the product requirements, the corresponding adhesive will be different.